| Animal Sciences Division | |
| Introduction | |
|
Pakistan is blessed with diversified animal resources. It includes farm animals, pets, birds and wildlife etc. The contribution of livestock to national GDP (11.8%), Agricultural GDP (55.9%), foreign exchange earnings (8.5%), and rural socioeconomic development of the country is significant. The Animal Sciences Division (ASD) at NIAB deals with different issues regarding livestock production and health. The Division comprises of Animal Nutrition Group, Animal Reproductive Endocrinology Group, Veterinary Drug Residue Group and Vaccine Development Group. | |
|
Animal Nutrition Feeding of animals represents one of the most important areas of animal production and feeding expenses may be up to 70% of total expenditure on livestock based enterprises. Research programme of this group are focused on minimizing the animal feeding expenses while optimizing the animal productivity. In this context, feed supplementation strategies have been introduced and urea molasses multinutrient block (UMMB) technology has been successful in field conditions. In Pakistan huge quantities of dietary fibre are offered to animals which results in poor performance. Use of fibre degrading enzymes for better utilization of fibrous feeds is also being studied in this group. Salinity is threatening sustainable land utilization in our country. Regarding saline livestock production extensive studies are being conducted for evaluation and feeding of non-conventional foliage produced on saline lands using brackish water. Another novel work of this group is the study of radioactivity transfer from plants to animals and animal based products. Work on production of amino acids like lysine and methionine etc. by fermentation is another attempt by which poultry sector can benefit from the findings of this group. Animal Reproduction and Endocrinology The general objective of the group is to improve the reproductive efficiency of farm animals through analytical research and field studies. Previously, radioimmunoassay method for the analysis of protein hormones of livestock was established and the effect of saline environment on reproductive parameters and endocrinology of Dwarf goat was studied. At present, particular concern is directed towards solving reproductive problems of livestock through estrus synchronization strategies. The analysis of reproductive hormones of farm animals is also performed with the aim to investigate the underlying reproductive issues of livestock. Research is also going on to explore the role of oxidative stress in relation to reproduction in animals. The purpose is to determine the changes in biomarkers of oxidative stress that regulate the reproductive and endocrine mechanisms. Veterinary Drug Residue An increase in the use of veterinary drugs including parasiticides (ecto/endo), antibiotics and growth promoters, is a predictable-consequence of expanded food/animal production efforts. These drugs leave their residues in animal tissues, biological fluids (serum, urine and milk) and need to be analyzed. Unfortunately, many of the developing countries suffer from lack of effective regulatory control of their use. Improper use of these chemicals can exceed safe residual limits in food derived from the treated animals. No doubt, quantity is important to feed such a large population of Pakistan, but quality is of equal importance. It requires full scientific evaluation of relative hazards as well as qualitative/quantitative analysis of veterinary drugs residues in livestock/poultry. It is possible by conducting systematic set of experimentations, standardizations and applications to food products/byproducts so as to ensure effective residual control in human food which is our research mandate. Vaccine Development The veterinary vaccines have had, and continue to have, a major impact not only on animal health and production but also on human health through increasing safe food supplies and preventing animal-to-human transmission of infectious diseases. The major goals of veterinary vaccines are to improve the health and welfare of companion animals and to increase the production of livestock in a cost-effective manner. Vaccine Development Group at NIAB is working on development and application of modified conventional and new technologies including gene-deleted, subunit, ‘naked’ DNA and vectored vaccines. Current research activities include development of subunit vaccine against Hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and buffalo and development of conventional and advanced vaccines against Hydropericardium syndrome (HPS), Infectious bursal disease (IBD) and Newcastle disease (ND) of poultry birds. We are planning to initiate research work on foot-and-mouth disease; a highly contagious and economically important disease of cattle and buffalo. [top] | |
|
(a) Animal
Nutrition 1. To study salt tolerant plants as forages for livestock 2. To develop supplementation strategies 3. To study the effect of feed additives 4. Exploring amino acid-fermenting bacteria for the up-gradation of industrial waste 5. Study the transfer functions of radioactivity from plants to animals (NIAB-PIEAS-PNRA)
(b) Animal Reproduction and Endocrinology 1. Development of estrus synchronization strategies in livestock 2. Studies on oxidative stress biomarkers related to reproduction in farm animals
(c) Veterinary Drug Residue 1. Amoxicillin, Cypermethrin, Deltamethrin, determination in meat & milk by HPLC 2. Effect of repeated administration of oxytocin on lactating buffaloes by ELISA 3. Chloramphenicol (CAP) determination in milk and meat of Faisalabad Region (d) Vaccine Development 1. Development of Vaccines and Diagnostic assays against important diseases of livestock and poultry | |
| Achievements | |
|
Nutritive value of Moringa and Barley | |
|
Among 13 species of Moringa, Moringa oleifera (family Moringaceae) is the most important commonly known as “Sohanjna” is native to South Asia and introduced into the tropics. The use of Moringa tree as an animal feed is not very common. Lush green stand of the trees even in the coldest periods of years shows the potential of the tree for the year around supply of the forage. Nutritive values of candidate barley varieties of NIAB were evaluated and intra-varietal difference in crude protein ranged from 5.16% to 13.37%. Similarly, the average crude fibre content was found as 26.1% varying from 17.5% to 32.5%. The ether extract was maximum (3.2%) in NBA-19 while minimum (1.8%) in NBA-16. The high difference found in nutritive values of candidate varieties offers their selection in respect of high production and nutrition. | |
|
Urea Molasses Multinutrient Blocks (UMMB) as a feed supplement | |
|
A study was conducted to enhance the milk production in the country by using Urea Molasses Multinutrient Block (UMMB). It is a (solidified) lick, which provides critical microbial nutrients to increase microbial fermentation in the rumen. This block is prepared from local, easily available and cheaper feed ingredients. The feeding trials of UMMB showed that there was a strong relationship between UMMB feeding and increase in daily milk production in lactating buffaloes. | |
|
Use of fibre degrading enzymes produced from Chaetomium thermophile for livestock production | |
|
The effect of enzyme supplementation on performance and nutrient digestibility were evaluated. The effect of enzyme supplementation on breeding goats was non-significant while in case of growing kids, there was 16.2% and 20.3% improvement in weight gain and feed conversion ratio (FCR). In sheep, enzyme supplemented group attained a 20.2% better weight gain and 11.76% narrower FCR compared with control. During metabolic studied, better apparent digestibility of dry matter, acid detergent fibre and neutral detergent fibre were observed in enzyme supplemented groups than control in both goat and sheep. | |
|
Up-gradation of Agro-Industrial Waste for Amino Acid Production through Bacteria | |
|
Majority of the wild type strains produced alanine, aspartic acid and glutamic acid upto 4.3, 2.5 and 1.8 g/L, respectively. In addition, some other amino acids, such as leucine, isoleucine, valine and histidine were also produced in traces. On the basis of their amino acid production potential, the isolates were mutated. Five mutants were tested for their ability to produce lysine in different molasses media. The effect of different glucose concentrations (5-15%) was investigated on lysine production in time course study. The results showed that the best lysine production was achieved with 10% glucose concentration at 30oC after 64 hours of incubation. Among the media tested for lysine production, MM (Molasses based media) provided better yield of L-lysine. Initially, the production of a wild type isolate, NIAB KN-98, was increased from negligible to a level of more than 3 g/L. For the production of glutamic acid, a strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum, NIAB SS-67 was used for the media optimization. The best glutamic acid production appeared at 10% glucose after 72 hr at 29+1°C. It was almost 2.5 fold increase from the initial production level, and it gradually decreased with the increase in glucose concentration. | |
|
Transfer of Radioactivity from Plants to Animals and Animal Products | |
|
Commercial RIA kits for the analysis of protein hormones of animals are not available in Pakistan. The RIA kits for humans do not work for the analysis of hormones of animals due to species specificity. To analyze protein hormones (LH & FSH) of livestock, a double antibody competitive RIA method has been standardized for the first time in Pakistan at NIAB which can be used for research on livestock. By using these methods, major reproductive hormones (progesterone, estradiol, LH and FSH) at different reproductive stages of a prolific breed of goat (Dwarf) have been analyzed to establish the normal baseline data. Based on this data, the reproductive parameters of this breed were assessed. These methods would facilitate the understanding of various physiological and reproductive aspects of livestock under different environmental/ nutritive conditions. Milk progesterone assay was also established for Early Pregnancy Diagnosis in cattle. |
|
|
Estrus Synchronization Strategies Goat Synchronization of estrous cycle of ruminants is a reproductive management tool to improve fertility. The estrous cycle of Dwarf goat was manipulated by estrumate injections under normal as well as saline environment. The results suggested that estrumate is an efficient synchronizing agent for the Dwarf goats kept under different management conditions and that the progesterone profile is a useful indicator to assess the reproductive status of goats. Estrous cycle of goats was also synchronized by methylacetoxy progesterone (MAP) sponges, prepared at NIAB. The MAP gave higher conception rate than control group indicating the improved fertility. It was concluded that the use of estrus synchronization strategies could further enhance the reproductive efficiency of Dwarf goat and enable the farmers to get a kid crop at faster rates. | |
|
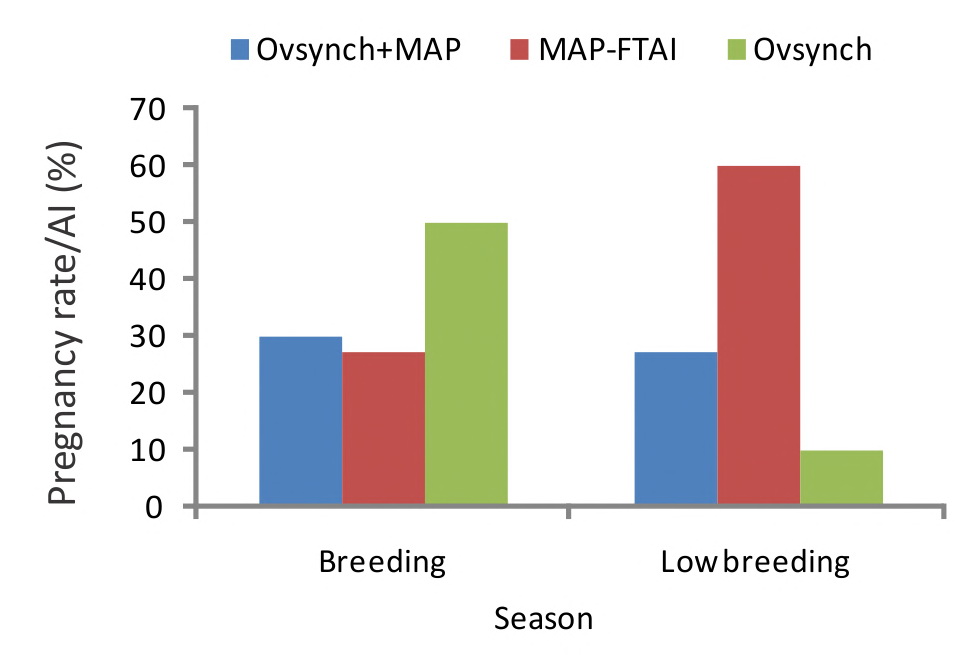
Buffalo Buffalo is the principal dairy animal in Pakistan. However, it is a poor breeder. Studies were performed to improve the reproductive performance of female buffalo using estrus synchronization strategies. The MAP sponges, prepared at NIAB, successfully synchronized estrous cycle in buffaloes. The use of these sponges in a timed breeding programme (MAP-FTAI) in buffaloes, in a comparative field trial at Sirbuland Livestock and Dairy Farm, proved that a significantly high pregnancy rate (60%) was achieved in buffaloes by MAP-FTAI protocol as compared to the Ovsynch (10%) and Ovsynch plus MAP (27.3%) protocols during low breeding season and these regimens gave higher pregnancy rates in cyclic than acyclic buffaloes. Their use in on farm timed breeding programme on large scale could improve conception rate and hence reproductive efficiency of the buffalo herds and may contribute in increasing the milk production during lean periods in the country. |
Fig: Pregnancy rate (%) after Ovsynch+MAP, MAP-FTAI and Ovsynch protocols in Nili-Ravi buffaloes during breeding season (BS) and low breeding season (LBS). |
|
|
|
|
Effect of repeated oxytocin administration on cGMP levels in lactating buffalos | |
|
cyclic-Guanosine Monophosphate (cGMP) that is an important intracellular secondary messenger/ regulator/ mediator involved in a number of biological reactions and metabolic processes. Effect of repeated administration of oxytocin on cGMP levels of lactating buffaloes was studied employing ELISA assay. |
|
| Blood samples were collected from oxytocin treated and untreated (control) buffaloes availabe at SB farm Theekriwala, Faisalabad. Standard protocols for sample analysis were followed (Sigma cGMP EIA kit Cat # CG201). Results showed that repeated administration of oxytocin did not necessarily increase cGMP levels, indicating animal resistance to artificial hormonal treatment. | |
|
Detection of Chloramphenicol in Muscles using Competitive ELISA | |
| Chloramphenicol (CAP) is highly effective antibiotic, widely used in veterinary medicine. A zero tolerance has been established for CAP residues in Dairy products. For this purpose, immunogen and enzyme tracer were prepared with Human Serum Albumin (CAP-HSA) and Horseradish Peroxidase (CAP-HRP). Sensitivity of antibodies was assessed by calculating IC50. Titer of three antibodies (S235, S236 and R877) and enzyme tracer was checked. Muscle samples were extracted in buffer, clean up by hexane. Preliminary studies showed its working range from 0 to 0.5 ng of CAP per g of muscle. This method was designed to select samples that may contain CAP above ½ MRPL (0.15 ng/g). |
|
|
Surveillance of outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease | |
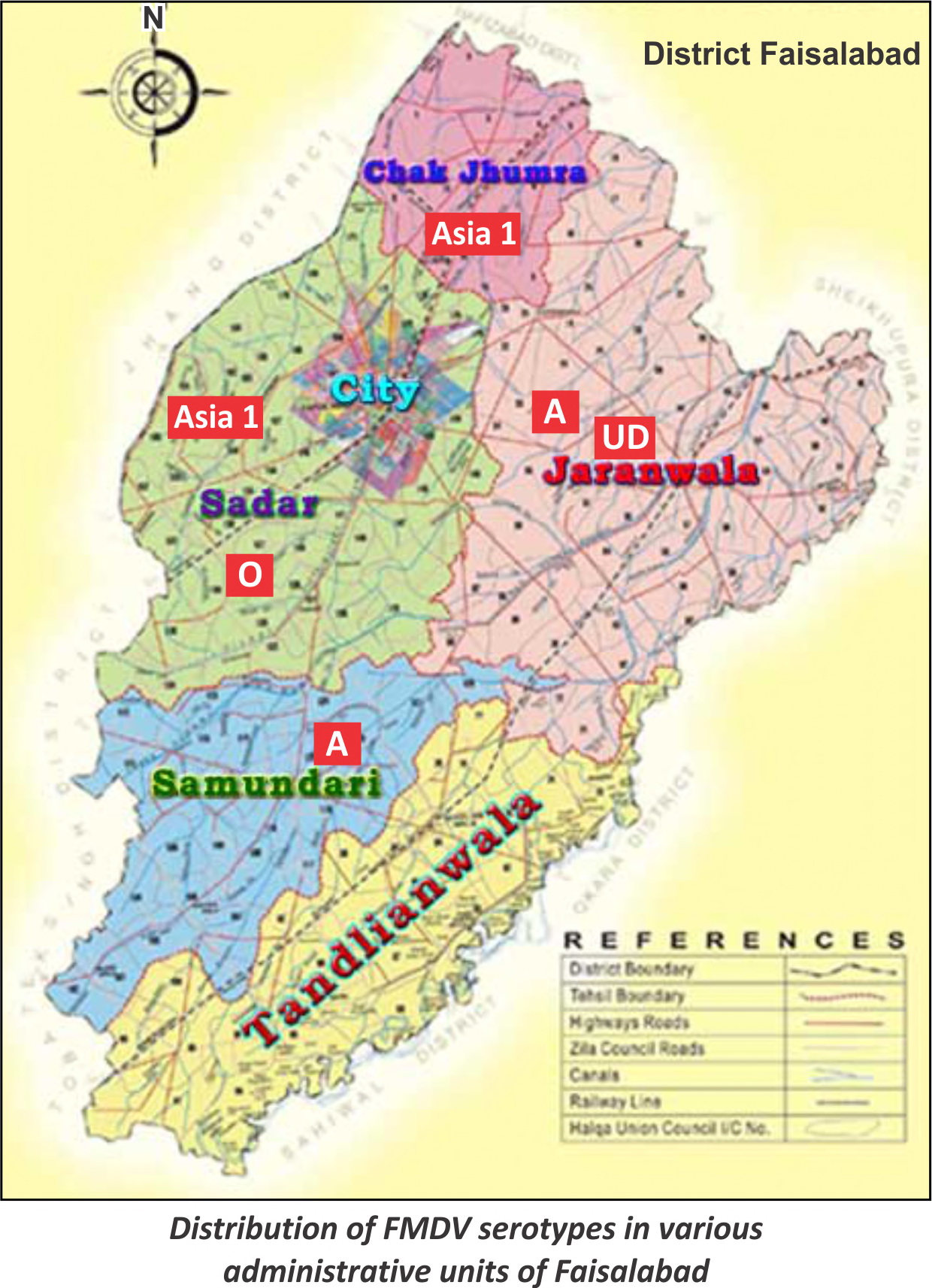
| Sampling was done from various outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease that occurred during 2013 in and around Faisalabad. Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used for typing of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). A total of 68 samples were received, 54 were found FMDV genome positive when tested with 1F and 1R consensus primers. Out of these genome positive samples 48 were successfully typed into types A (12 samples), O (20 samples) and Asia 1 (16 samples). Complementary DNAs (cDNAs) were stored at -80°C for further sequencing studies. Type A serotype was detected from samples received from Sumandri and Jaranwala tehsils, type O from Sadar, and Asia 1 outbreaks were reported from Chak Jhumra and Sadhar. |
|
|
Isolation, identification and molecular characterization of Newcastle Disease (ND) virus from field outbreaks | |
|
Clinical samples were collected from suspected poultry farms around Faisalabad. Samples were processed for isolation of ND virus in chicken embryonated eggs and presence of the virus was confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Partial F-gene was amplified and nucleotide sequence of variable region was determined. Phylogenetic analysis of variable region of F-gene revealed that our isolates belong to highly pathogenic ‘velogenic viscerotropic’ Newcastle disease virus. Further work on adaptation/propagation of the virus in suitable system is underway. |
|
|
A subunit vaccine against hydropericardium syndrome using adenovirus penton capsid protein | |
|
Hydropericardium syndrome (HPS) is a disease of poultry that is caused by fowl adenovirus-4. Inactivated liver homogenate from diseased birds is still the choice of vaccine in some countries which disseminates numerous pathogens along with inactivated virus. Moreover incomplete attenuation or inactivation, reversion to virulence and the oncogenic potential/genetic instability of the adenoviruses have prevented their use in routine vaccines. To address this problem an effort is made to develop a subunit vaccine. For this purpose penton base protein of HPS virus was expressed in Escherichia coli and used as subunit vaccine in broilers. Immunogenicity of the recombinant penton base protein and challenge protection test against pathogenic virus demonstrated the ability of recombinant penton base protein to confer (90%) protection. Results suggest that the recombinant penton base protein is a candidate for subunit vaccine against HPS. | |
|
Immunogenecity of Lipopolysaccharide form Pasteurella multocida against Haemorrhagic Septicaemia | |
|
Haemorrhagic septicemia (HS) is a fatal disease of cattle and buffaloes that result in heavy economic losses. Pasteurella multocida is causative organism of the disease. P. multocida was cultured on casein sucrose yeast (CSY) medium and the LPS was isolated by proteinase K digestion method. The isolated LPS were quantified by using semi-carbazide method and periodic acid method. Then this quantified antigen was injected into rabbits for antibody production. The serum samples were collected and antibody titer was checked by using Indirect ELISA. It was found that with increase in LPS antigen, the antibody titer increased and the combination of LPS of P. multocida with yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) has induced more immunity as compared to LPS alone in rabbits. Hence it was found that the LPS was immunogenic and its immunogenic activity can be slightly improved by addition of carrier proteins from yeast. |
|